34 MENOPAUSE SYMPTOMS |
HEALTH CENTER |
|
| |
|
|
|
Testosterone Patch may Alleviate Low Libido |
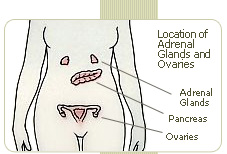
Loss of libido (in medical terminology, "hypoactive sexual desire disorder") in women is often linked to decreased levels of testosterone hormones. The ovaries and adrenal glands produce 50% of testosterone, but during menopause this production decreases dramatically, leading to reduced sexual activity and desire in menopausal women. Roughly forty percent of women report loss of libido during and after menopause. This is even more dramatic in women who have undergone oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries): after surgery, testosterone levels fall fifty percent lower than before.
|
 |
|
|
|
Estrogen therapy can help to alleviate sexual problems like vaginal dryness and vaginal atrophy after oophorectomy, but this alone will not necessarily alleviate loss of libido. It appears that adequate levels of testosterone are also necessary for women to maintain healthy sexual activity.
Various forms of testosterone therapy have been tested for women with low libido, including oral administration (pills) and injections. John Buster et al conducted a study published in the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology testing the efficacy of a low-dose testosterone patch, and conclude that this is a particularly viable option for treating low libido in postmenopausal women.
|
|
The study followed 533 women who reported loss of libido after undergoing hysterectomy and oophorectomy, and had already been receiving estrogen therapy for the past 3 months. Subjects were all in a stable, long-term relationship with a sexually available partner. 266 women were placed in the control group, while 267 test subjects were administered the testosterone patch.
Results were tested by having the patients keep a Sexual Activity Log diary over a 24 week period, to be measured against the Profile of Female Sexual Function , which gauged 7 distinct categories of sexual function: sexual desire, sexual pleasure, sexual arousal, orgasm, sexual responsiveness, sexual concerns, and sexual self-image. Blood tests measured testosterone and estrogen levels. Subjects were also monitored for androgen affects such as facial hair, acne, and headache. |
The study concluded that the testosterone patch produced significantly positive results in terms of increasing libido after 24 weeks. Bestresults were achieved after 12 weeks and continued through the rest of the 24-week period. By week 24, women in the test group reported improvement in all 7 categories of sexual function. Sexual desire increased on average by 49%, while total orgasms increased 68%.
|
Common undesirable side effects included headaches, increased facial hair, and skin reaction to the application of the patch, but incidence was rare and reported as moderate. Furthermore, because the study lasted only 24 weeks, safety of the treatment beyond this period cannot be guaranteed. It should also be remembered that test subjects were also receiving estrogen therapy, which may have guarded against some of the androgen affects of testosterone.
The study also found that the administration of testosterone by patch is most likely superior to administration via oral consumption, implant, or by injection, which may deliver elevated and unstable levels of testosterone. The patch, on the other hand, delivered a low, constant, controlled dose of the hormone.
By Natural-Progesterone-Estrogen-Supplements.com |
 |
|
|
|
|
| |
Copyright� 2008 - - All Rights Reserved |
|
|